RES JUDICATA
TANMOY MUKHERJEE INSTITUTE OF JURIDICAL SCIENCE
Dr. Tanmoy Mukherjee
Advocate
RES JUDICATA
TANMOY MUKHERJEE
[ADVOCATE]

According to Section 11 of the Civil Procedure Code, 1908-
‘No Court shall try any suit or issue in which the matter directly and substantially in issue has been directly and substantially in issue in a former suit between the same parties, or between parties under whom they or any of them claim, litigating under the same title, in a Court competent to try such subsequent suit or the suit in which such issue has been subsequently raised, and has been heard and finally decided by such Court.
- Explanation I .-The expression "former suit" shall denote a suit which has been decided prior to the suit in question whether or not it was instituted prior thereto.
- Explanation II.-For the purposes of this section, the competence of a Court shall be determined irrespective of any provisions as to a right of appeal from the decision of such Court.
- Explanation III.-The matter above referred to must in the former suit have been alleged by one party and either denied or admitted, expressly or impliedly, by the other.
- Explanation IV.-Any matter which might and ought to have been made ground of defence or attack in such former suit shall be deemed to have been a matter directly and substantially in issue in such suit.
- Explanation V.-Any relief claimed in the plaint, which is not expressly granted by the decree, shall, for the purposes of this section, be deemed to have been refused.
- Explanation VI .-Where persons litigate bona fide in respect of a public right or of a private right claimed in common for themselves and others, all persons interested in such right shall, for the purposes of this section, be deemed to claim under the persons so litigating.
- Explanation VII .-The provisions of this section shall apply to a proceeding for the execution of a decree and references in this section to any suit, issue or former suit shall be construed references, respectively, to a proceeding for the execution of the decree, question arising in such proceeding and a former proceeding for the execution of that decree.
- Explanation VIII .-An issue heard and finally decided by a Court of limited jurisdiction, competent to decide such issue, shall operate as res judicata in a subsequent suit, notwithstanding that such Court of limited jurisdiction was not competent to try such subsequent suit or the suit in which such issue has been subsequently raised. References, respectively, to a proceeding for the execution of the decree, question arising in such proceeding and a former proceeding for the execution of that decree.
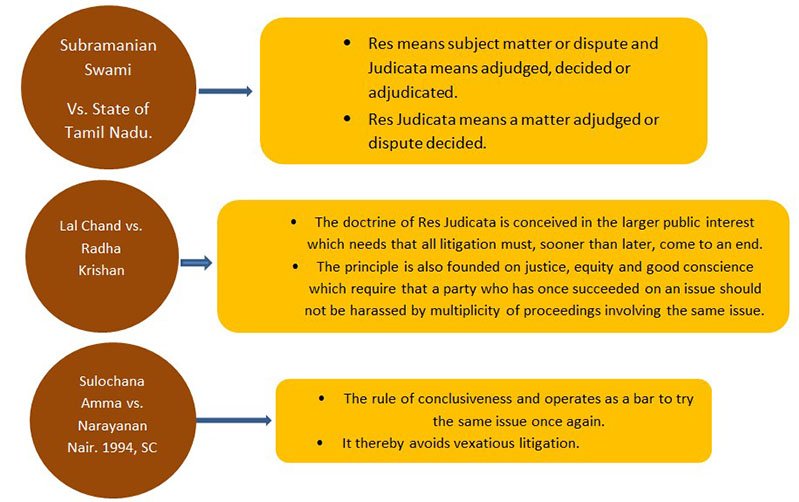
The doctrine of Res Judicata is mainly based on three maxims, which are non- negotiable in any civilized system of law-
- Nemo debet bis vexari pro una et eadem causa (no man should be vexed twice for the same cause).
- Interest reipubicae ut sit finis litium (it is in the interest of the State that there should be an end to a litigation), and
- Res judicata pro veritate occipitur (a judicial decision must be accepted as correct).

Illustration:
- A sues B for possession of certain properties on the basis of a sale deed in his favor. B impugns the deed as fictitious. The plea is upheld and the suit is dismissed. A subsequent suit for some other properties on the basis of the same sale deed barred as the issue about the fictitious nature of the sale deed was actually in issue in the former suit directly and substantially.
- A sues B, C and D and in order to decide the claim of A, the court has to interpret a will. The decision regarding the construction of the will on rival claims of the defendants will operate as res judicata in any subsequent suit by any of the defendants against the rest.
- Case References :




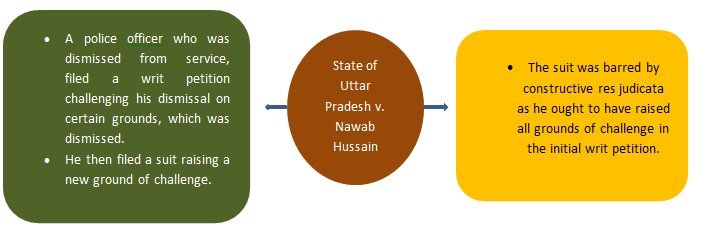
- Constructive Res Judicata-
Key Elements -
For the principle of constructive res judicata to apply, the following conditions must be met:
- A Former Suit: There must have been a formerly decided lawsuit.
- Same Parties: The parties in the subsequent suit must be the same or litigating under the same title as in the former suit.
- Competent Court: The court that decided the former suit must have been competent to try it.
- "Might and Ought to have been Raised": The matter being raised in the subsequent suit must be one that the party could have raised and was obligated to raise as a ground of attack or defense in the earlier suit.
Reference Cases-
Detailed Distinction-
|
Feature
|
Res Judicata
|
Constructive Res Judicata
|
|
Basis
|
Bars re-litigation of issues actually heard and decided.
|
Bars re-litigation of issues that might and ought to have been raised but were not.
|
|
Scope
|
Narrower, applies to matters clearly adjudicated.
|
Broader, applies to matters deemed to have been decided by implication.
|
|
Focus
|
On what was decided.
|
On what should have been decided.
|
|
Section
|
Section 11 of the CPC.
|
Explanation IV to Section 11 of the CPC.
|







