The duties (functions) of the Finance Commission
Dr. Tanmoy Mukherjee
Advocate
The duties (functions) of the Finance Commission-
Tanmoy Mukherjee
Advocate

The Finance Commission is a constitutional body established under Article 280 of the Constitution of India. It plays a crucial role in maintaining financial equilibrium between the Union and the States and in strengthening fiscal federalism. The Commission acts as an impartial and expert body to recommend principles governing the distribution of financial resources in India.
Constitutional Basis-
Article 280(1) – Mandates the President to constitute a Finance Commission every five years or earlier.
Article 280(2) – Provides for the composition of the Commission.
Article 280(3) – Enumerates the duties/functions of the Finance Commission.
Article 275 – Grants-in-aid to States.
Duties / Functions of the Finance Commission-
1. Distribution of Net Proceeds of Taxes
[Article 280(3)(a)]
(a) Vertical Distribution-
Recommends division of net proceeds of taxes between:
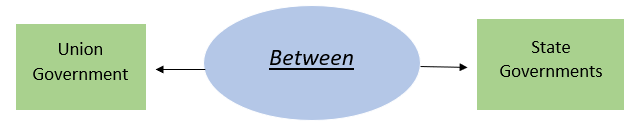
(b) Horizontal Distribution-
Allocation of States’ share among individual States based on:
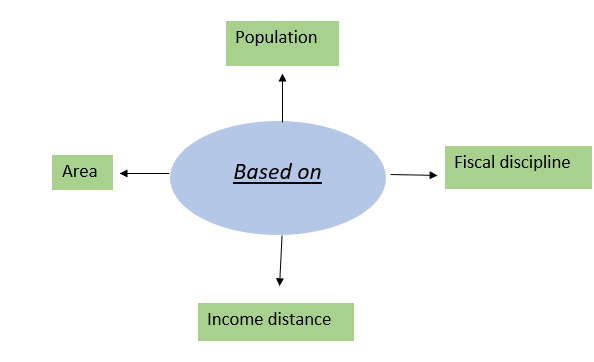
Reference Case-
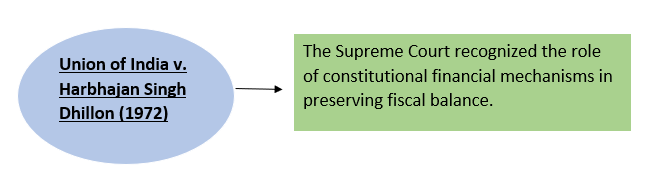
2. Principles Governing Grants-in-Aid to States-
[Article 280(3)(b) read with Article 275]
Recommends grants to States which:
→Have revenue deficits
→Require assistance for special needs
→Ensures minimum standards of governance across States.
Reference Case-
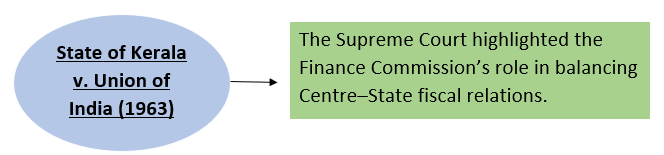
3. Strengthening Panchayats’ Financial Position
[Article 280(3) (bb)]
→Inserted by the 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992.
→Recommends measures to augment resources of Panchayats.
→Based on recommendations of State Finance Commissions.
Reference Case-
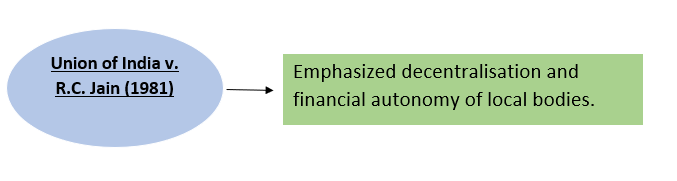
4. Strengthening Municipalities’ Financial Position-
[Article 280(3)(c)]
→Inserted by the 74th Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992.
Ensures adequate funding to:
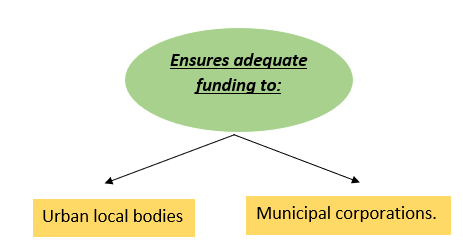
Reference Case-
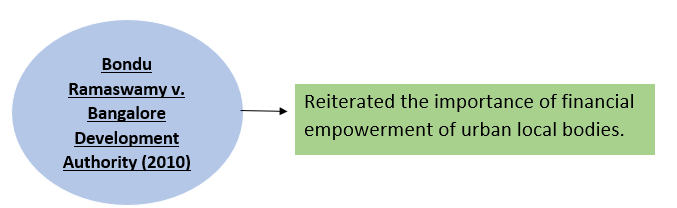
5. Maintenance of Fiscal Discipline-
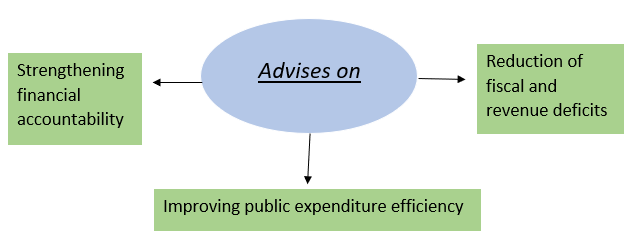
Promotes sound finance and long-term economic stability.
Reference Case-
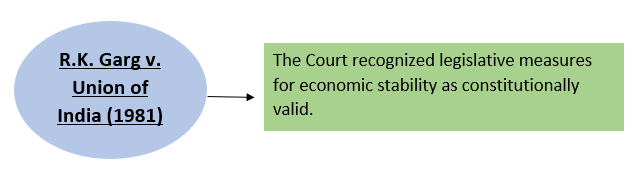
6. Recommendations on Public Debt and Financial Stability-
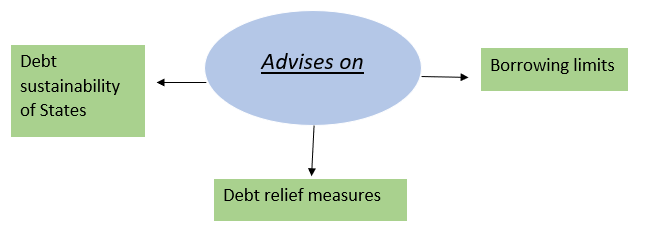
Reference Case-
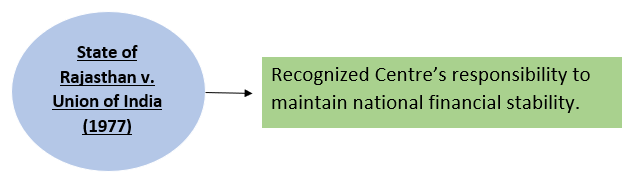
7. Measures to Promote Cooperative Federalism-
→Encourages cooperation rather than conflict between Centre and States.
→Ensures equitable development of backward regions.
Reference Case-
8. Advisory Role on GST Compensation-
→After the 101st Constitutional Amendment, Finance Commission:
→Advises on revenue loss due to GST
→Suggests compensation mechanisms
Reference Case-
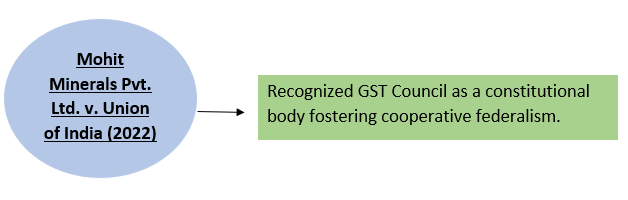
9. Any Other Matter Referred by the President-
→ [Article 280(3)(d)]
The President may refer:
→Disaster management funding
→Climate finance
→Special economic packages
This clause gives the Commission flexibility.
Reference Case-
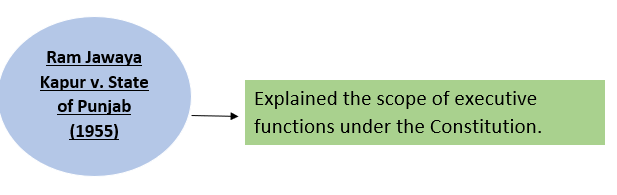
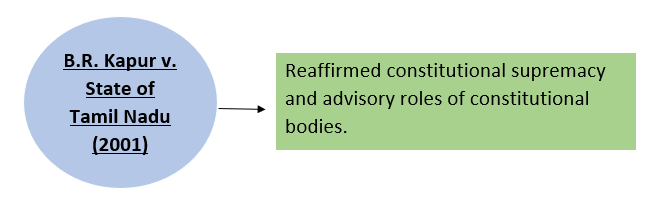
10. Nature of Recommendations-
→Recommendations are advisory, not binding.
→However, due to constitutional authority, they are usually accepted.
Reference Case-
Importance of the Finance Commission
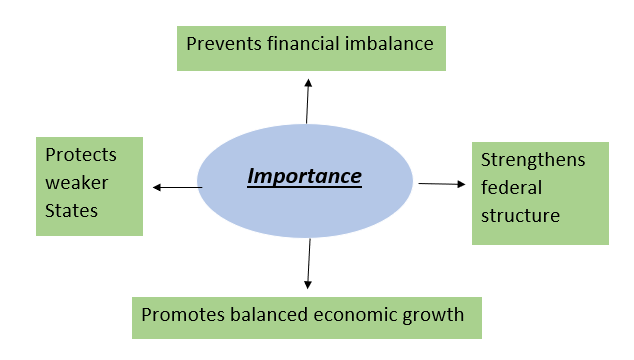
The Finance Commission occupies a central position in India’s fiscal federal structure. Through its duties under Article 280, it ensures equitable distribution of resources, strengthens local self-government, promotes fiscal discipline, and sustains cooperative federalism. Though its recommendations are advisory, in practice they shape India’s financial governance and national unity.